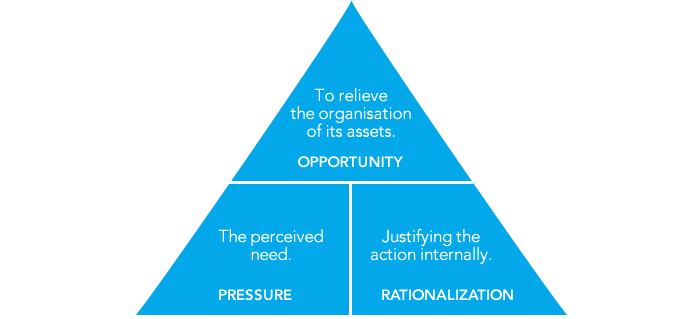
Introduction: A Case That Needed Answers
In 2010, a cooperative society faced allegations of financial mismanagement and fraud. At the center of the controversy was the repair of an overhead water tank—a seemingly routine maintenance task that revealed systemic irregularities. As a forensic accountant, I was brought in to unravel the truth. This case is a testament to how forensic accounting can expose the layers of deceit hidden in plain sight.
This case study takes you through the investigation, the challenges faced, and the lessons learned.
The First Signs of Trouble: A Routine AGM Raises Questions
The story begins in July 2010, during the Annual General Meeting (AGM) of the cooperative society. The meeting resolved to repair the overhead water tank, but the minutes lacked critical details about costs, contractor selection, and tendering processes—a red flag for transparency. By August 2010, concerns began to mount among society members.
Key Issues Identified
Lack of transparency in meeting minutes.
Missing details about contractor selection.
Bylaw violations concerning financial disclosures.
Unveiling the Web: Suspicious Contractor Quotations
In October 2010, two contractor quotations emerged, both dated the same day and originating from companies sharing the same address. This raised immediate suspicions about the legitimacy of these firms.
Observations
- The absence of detailed cost breakdowns.
- A shared address for two supposedly independent contractors.
Approval and Payment: The Plot Thickens
By November 2010, the society’s Working Committee approved repairs for ₹1,30,000 without consulting members. Payments were issued via bearer cheques—a method bypassing transparency norms and society bylaws.
Investigative Findings
- Cheques totaling ₹81,100 were signed by key committee members but withdrawn by an unaffiliated individual.
- Signature discrepancies on cheque endorsements indicated forgery.
The Forensic Approach: Connecting the Dots
As a forensic accountant, my role was to sift through documents, identify anomalies, and connect the seemingly unrelated dots. Each piece of evidence pointed toward deliberate financial mismanagement.
Techniques Employed
Document Analysis
Reviewed AGM minutes, contractor quotations, and payment records.
Signature Verification
Conducted forensic handwriting analysis, revealing forgery.
Transaction Tracing
Followed the money trail to identify unauthorized withdrawals.
False Narratives: Misrepresentation to Members
Circulars issued in December 2013 claimed payments were made via cheques, contradicting the actual bearer cheque transactions. The committee’s deliberate misrepresentation further complicated the accountability trail.
Evidence Highlights
- Circular discrepancies exposing false claims.
- Meeting minutes misrepresenting key facts.
Legal and Regulatory Breaches
This case wasn’t just about mismanagement; it also highlighted violations of multiple laws
Society Bylaws
Transactions above ₹1,500 were required to be made via cross-cheques.
Indian Contract Act
The absence of contractor legitimacy undermined the contract’s validity.
Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA)
Issuing bearer cheques to fictitious entities suggested attempts to disguise financial misconduct.
Negotiable Instruments Act
Forged endorsements invalidated the cheques under Section 87.
Resolution: Bringing Accountability
After presenting a detailed report, including forensic evidence and legal violations, the findings were submitted to the appropriate authorities. The implicated committee members were held accountable for their actions, ensuring justice and transparency for the society.
Lessons Learned: Red Flags to Watch For
This case underscores the importance of vigilance in financial transactions. Here are key takeaways
Transparency in Decision-Making
Always document and disclose critical decisions.
Due Diligence
Verify the legitimacy of contractors and transactions.
Adherence to Bylaws
Financial governance rules exist for a reason.
Forensic Investigation
The power of detailed analysis can unravel even the most complex frauds.
Conclusion: The Power of Forensic Accounting
This case serves as a reminder that financial integrity is non-negotiable. As forensic accountants, we play a crucial role in safeguarding organizations from fraud and ensuring accountability. While the journey was challenging, the resolution brought peace of mind to the society members and reaffirmed the importance of transparency.
This is one of many stories where forensic accounting serves justice and restores trust. Stay vigilant, and remember—the numbers never lie, but they do require interpretation.